
What is a pelletizer?
1.Strand cut
2.Water-cooled hot cut(watering hot cut)
3.Underwater cut
Extruders equipped with the latest hot cut system
What is a pelletizer?
Pelletizing is the process of cutting resin into pellet-shaped pieces.
A pelletizer is the name of the machine device that performs pelletizing.
The scrap that has been crushed in the shredding process passes through the screw of the extruder while being mixed, and is melted. The melted resin is extruded from the die at the tip, and then cut by a rotating blade at the end. This device that cuts with a rotating blade is called a pelletizer, and the method is roughly divided into three types.
We will also show you the difference between strand cut and hot cut below.
Reference article: Explanation of the structure of extruders
.png) |
 |
 |
1. Strand cut
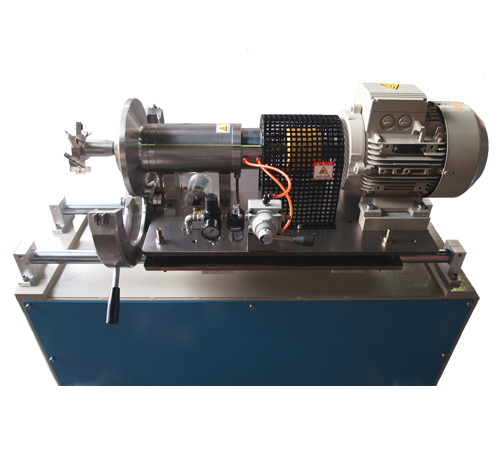
This is the most representative and oldest pelletizing method. The melted recycled resin is extruded from the die like spaghetti.
This is called a strand. The strands are cooled immediately by water in a water tank as shown in the photo below.
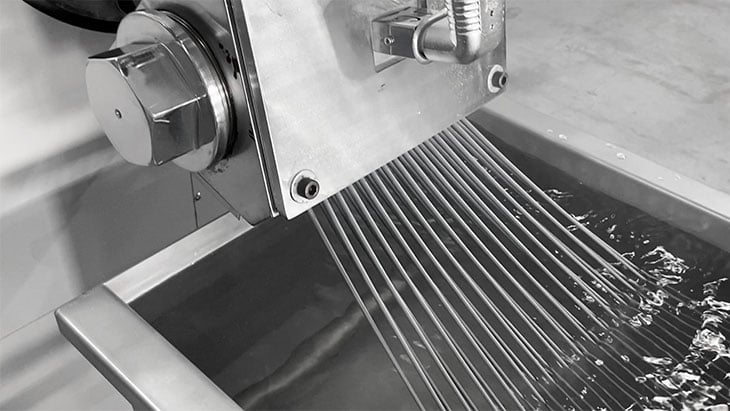

This is the most representative and oldest pelletizing method. The melted recycled resin is extruded from the die like spaghetti.
This is called a strand. The strands are cooled immediately by water in a water tank as shown in the photo below.

Strand Pelletizer
Points to note when using recycled pelletizers
If there are foreign objects, this spaghetti-like strand will break.
Other causes of strand breakage are moisture contamination or foaming (gas entering the resin).
Materials with a lot of contaminants cannot be processed by this strand cut method.
The main causes of strand breakage
- Foreign matter (contamination) contamination
- High moisture content (more than 3%)
- Gas generating substances
Conversely, if you say that only strands are purchased by users (only some), it can be said that there are few foreign substances, little foaming, and dry in the pellets made by strand cutting. (This is why strand-cut pellets are sometimes preferred)
- Advantages: There are few foreign substances in the pellets made Some users only buy this strand (only some)
- Disadvantages: It takes some skill to pull out the strands. It takes a lot of manpower (not so much if there are few foreign substances) Materials with a lot of foreign matter are not suitable for processing because the strands break
I wrote that it takes some skill to pull out the strands, but it’s not a difficult technique. The worker just scoops up the resin that comes out of the die (the end of the extruder) with their hand and pulls it to the entrance of the pelletizer.
At this time, you need to “carry it at an appropriate constant speed” so that the strands do not become thick or thin. Then, before putting it into the pelletizer, you need to cut the strands with scissors, but you also need to “do both tasks at the same time”. It’s not a big deal if you get used to it, but if you’re new to it, you might say “it’s difficult”. I don’t know if this example is appropriate or not, but I think it takes about as long as “the first time you practice riding a bicycle”.
Strand cutting is suitable for materials with stable resin properties.
Conversely, as a disadvantage, it takes time to neatly arrange many strands so that they do not overlap or cross each other. If it is a small extruder, there are not so many numbers, but if it has a production capacity of more than 300kg/h per hour, there will be many numbers of strands.
Even if you arrange the strands neatly once, they sometimes break, stick together, or overlap. In that case, there is no choice but to fix it by hand.
Therefore, strand cutting has many work processes that require workers’ management.Point☛ If there are not many foreign substances and the strands do not break, it does not take much trouble
Point:If there are not many foreign substances and the strands do not break, it does not take much trouble
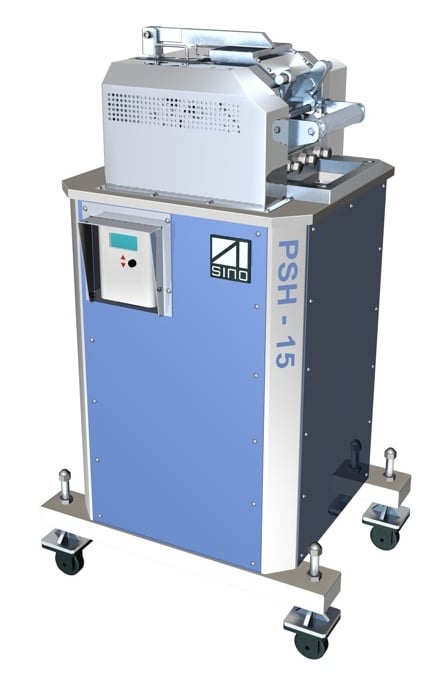
2. Water-cooled hot cut (watering hot cut)
The melted recycled resin that comes out of the die is cut by a rotating blade in a die inside the pelletizer.
This method is called water cut or underwater cut. Unlike the water-cooled hot cut, the resin is cut underwater without being exposed to air.
The pellets cut in the water are carried by circulating water and dehydrated by a dehydrator.
Previously, strand cutting was mostly used, but water-cooled hot cutting has gradually increased its share over the past 30 years or so.
Especially for recycled PE resins, I have the impression that the proportion of cases where water-cooled hot cutting is often used is high.

Pelletizer For hot cut
- Advantages: Less labor-intensive than strand type Can pelletize even if there are foreign objects Less work processes that require workers’ management (can be labor-saving)
- Disadvantages: Blade adjustment is difficult (click here for information on pelletizers that do not require adjustment) Blade maintenance is required Users may suspect that there are foreign objects in it (in the case of recycling)
The biggest strength and weakness of water-cooled hot cutting is that “it can be pelletized even if there are foreign objects”. For materials (scrap) that would break the strand in the strand cut method, hot cutting can be used to pelletize. (Of course, I’m not saying “I can do anything”)
However, on the other hand, users (buyers) who buy pellets may sometimes doubt that “I don’t know what’s in it”. In such a case, you need to dispel their doubts by showing them the manufacturing process, the original material and management status of the scrap, etc.
Also, some European and Taiwanese pelletizers have introduced technology that allows automatic blade adjustment, but other water-cooled hot cuts require manual blade adjustment by workers. “Blade adjustment” means that if the blade does not touch (contact) the die at the proper angle and pressure, pelletizing will not go well. This adjustment requires some skill, and if a skilled worker A adjusts it, there will be no trouble, but if another worker B does it, trouble will occur frequently. Once the adjustment is done well, no manpower is required, but it takes time to acquire the adjustment skills.
(Click here for information on pelletizers that do not require adjustment)
Point:If you want to pelletize materials with a lot of foreign matter, water-cooled hot cutting is less troublesome.
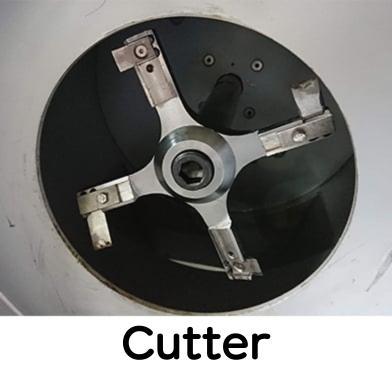
3. Underwater cut
The die in the pelletizer is in contact with hot water, and the recycled resin that comes out of the die is cut by a rotating blade underwater.
This method is called underwater cut or underwater cut. Unlike the above-mentioned water-cooled hot cut, the resin is cut underwater without being exposed to air.

Underwater cut (underwater cut)
Advantages: Can make pellets even with low viscosity resin
Disadvantages: High price (quite expensive)
The pelletizer mixes and melts the resin and finishes it at the end. Depending on the user, there may be detailed specifications for shape and other aspects, so you need to select a pelletizer after organizing and understanding information such as user needs and requirements standards and conditions.
Reference article: About the structure of extruder screw
Extruders equipped with the latest hot cut system
We introduce four models of POLYSTAR equipment equipped with this latest pelletizing system.
Pelletizer Repro-Flex (for film)
This is a pelletizer that is ideal for film recycling. You can choose either strand or water-cooled hot cut method.
Pelletizer Repro-One Integrated with crusher
You can pelletize lumps, non-woven fabrics, molded products, etc. without pre-treatment while crushing them. You can choose either strand or water-cooled hot cut method.
Pelletizer Repro-Direct Universal type
A universal type extruder that is suitable for any resin and any shape.You can choose either strand or water-cooled hot cut method.
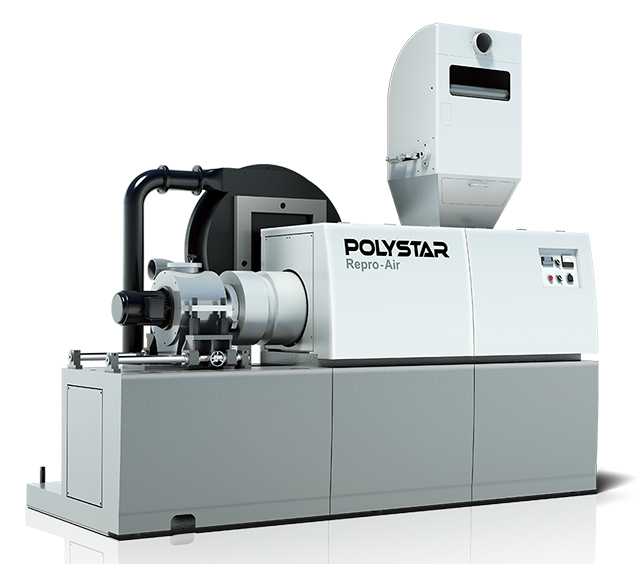
Pelletizer Repro-Air Ultra-small air-cooled type
An extruder that is ideal for recycling on the side of the production line in an inflation plant It is not water-cooled hot cut, but air-cooled hot cut.
List of extruder manufacturers
High price range
- Japan Steel Works, Ltd. (Japan,https://www.jsw.co.jp/en/)
- Shibaura Machine Co., Ltd. (Japan,https://www.shibaura-machine.co.jp/en/)
- CTE Co., Ltd. (Japan,http://www.cte-japan.net/en/)
- Technovel Corporation (Japan,https://www.technovel.co.jp/en/)
- Ikegai Corporation (Japan,http://www.ikegai.co.jp/en/)
- Coperion GmbH (Germany, https://www.coperion.com/en)
- Leistritz AG (Germany, https://www.leistritz.com/en/start)
- Milacron Inc. (Germany, https://www.milacron.com/)
Medium price range
- SINO-ALLOY MACHINERY INC.(Taiwan, https://www.sinoalloy.com/en/home-2/)
- Zenix Industrial Co., Ltd.(Taiwan, https://www.zenix.com.tw/)
- POLYSTAR MACHINERY INC (Taiwan,https://www.polystarco.com/en/about_C03.html)
- Freesia Macross Corporation (Japan, http://www.freesiamacross-extruder.com/en/)
Low price range
- NANJING COWIN EXTRUSION MACHINERY CO.,LTD.
(China, https://www.cowinextrusion.com/) - STEER Engineering Pvt Ltd(India, https://www.steerworld.com/)







Comment