| 1.What is an extruder? | Structure and mechanism. A brief explanation of the principle of extrusion. |
| 2.Applications of extruder | You can learn how they are used for different purposes. |
| 3.Extruder and die | The type of die determines the product shape that can be molded. |
| 4.Types of extruder | They vary depending on the purpose and application. |
| 5.Extruder equipment | An explanation of the hopper, feeder, screw, vent, etc. |
| 6.Extruder operation automation and labor saving | An introduction of the equipment for reducing labor. |
| 7.Extruder and pellets | An explanation of the distinction of pellets by the extruder method. |
| 8.Troubles related to extruder | An explanation of troubles such as vent up, surging, etc. |
| 9.Q&A about extruder | The difference between single-screw and twin-screw, hot cut and strand, etc. |
| 10.List of manufacturers | A list of manufacturers is provided. |
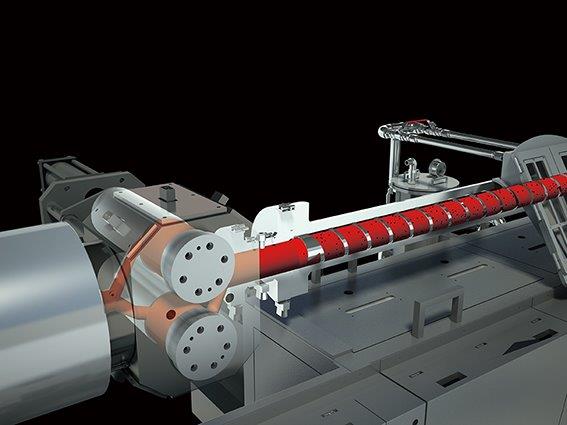
1.What is an extruder? Structure and mechanism
An extruder is a machine that melts plastic in a cylindrical steel chamber (cylinder) that is nitrided, and extrudes it from a mold at the end of the chamber (die) while mixing it with a screw. It is a general term for machines that mold plastic products into various shapes by cooling and molding the molten plastic.
2.Applications of extruder
The extruder itself has the same structure with a barrel and a screw for any application, but the products that can be processed vary depending on the shape of the die attached to the tip of the heating cylinder.
Types of molding methods using extruder
- Pelletizing for pellet production
- Rod-shaped extrusion molding
- Inflation molding for film production
- Injection molding using molds
3.Extruder and die
| Die shape | Product shape | Molding method name |
| Many small circular holes | Strand pelletizing | Pellet processing, a type of extrusion molding |
| Circular hole | Pipe | Extrusion molding |
| Thin line | Film, membrane | Inflation molding |
| Mold | Various | Inflation molding |
In recent years, 3D printers have been added as a new molding method, which continuously extrude molten resin from a thin nozzle and shape it.
4.Types of extruder
Extruder have various variations depending on the purpose and application.
1) Classification by the number of screws
There are simple types with one screw (single-screw extruder) and types with two screws that mix well (twin-screw extruder). Generally, when there is one screw, it is used for molding or pelletizing resin. When two screws are used, it is often used when you want to mix resin well.

Reference article: Explanation of single-screw extruder and twin-screw extruder
2) Classification by the pelletizing method
There are three main types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Strand method: The molten resin that comes out of the die is cooled in a water tank and cut
- Hot cut method: A rotating cutter above the die cuts the resin
- Underwater cut method: A cutter above the die that is in contact with water cuts the resin
Reference article: Explanation of three pelletizer methods
3) Classification by the number of extruders
Usually there is one extruder, but especially in the recycling industry, two are connected or sometimes three are connected. Recycling connects two because scraps often contain foreign matter, different resins, moisture, etc., and various problems occur. There is an effect of reducing problems by making it two-stage, so two-stage may be selected in the field of recycling.
1) Differences between single-screw extruder and twin-screw extruder (classification by the number of screws)
The classification by the number of screws mainly divides into single-screw extruders (one-axis extruders) with one screw and twin-screw extruders with two screws that mix well.
Reference article: Article on the difference between pellets made by single-screw extruder and twin-screw extruder
Single-screw extruder
It is an extruder that uses only one screw. It is the most widely used type. In the field of recycling, it is used as a primary processing for processing scrap into pellets for the first time. The screw is made from a single piece of steel. Also, inflation, extrusion molding, injection molding, etc., which mold products, use mostly single-screw extruders. Single-screw extruders are suitable for molding products because the pressure to extrude resin is stable.
Twin-screw extruder
Twin-screw extruder is an extruder that uses a pair of screws. It is characterized by its excellent resin kneading. Therefore, it is used when the dispersion and homogeneity due to its good kneading are important when manufacturing blended materials by coloring the material, modifying it with additives, or blending multiple resin materials. The screw can be changed to various combinations according to the purpose by using multiple different parts in a comb shape.Twin-screw extruder is used for processing called coloring or compounding. Generally,Twin-screw extruder are more expensive than Single-screw extruder.
Reference article: What is a Twin-screw extruder? Introduction of biaxial extruder
Reference article:What is a Twin-screw extruder? Introduction of Twin-screw extruder.
1.5-axis extruder
This is the type that combines the above single-screw extruder and twin-screw extruder. It is an extruder that combines one long screw and one short screw. From the material inlet to the middle of the barrel, there are two screws, but it becomes a single axis from the middle. It can perform good mixing and kneading in the twin-screw part, and stable extrusion in the single-screw part. It is very effective for manufacturing carbon-carbon composites and wood powder compound pellets.
Reference article:A comprehensive explanation of the structure, length, thickness, design, and types of extruder screws used in plastic recycling.
2) Classification by pelletizing method
Strand cut
Extrude the resin into spaghetti-like shape from the hole opened at the tip of the die and cool it in a water tank. Cut it with a pelletizer placed ahead to make pellets.
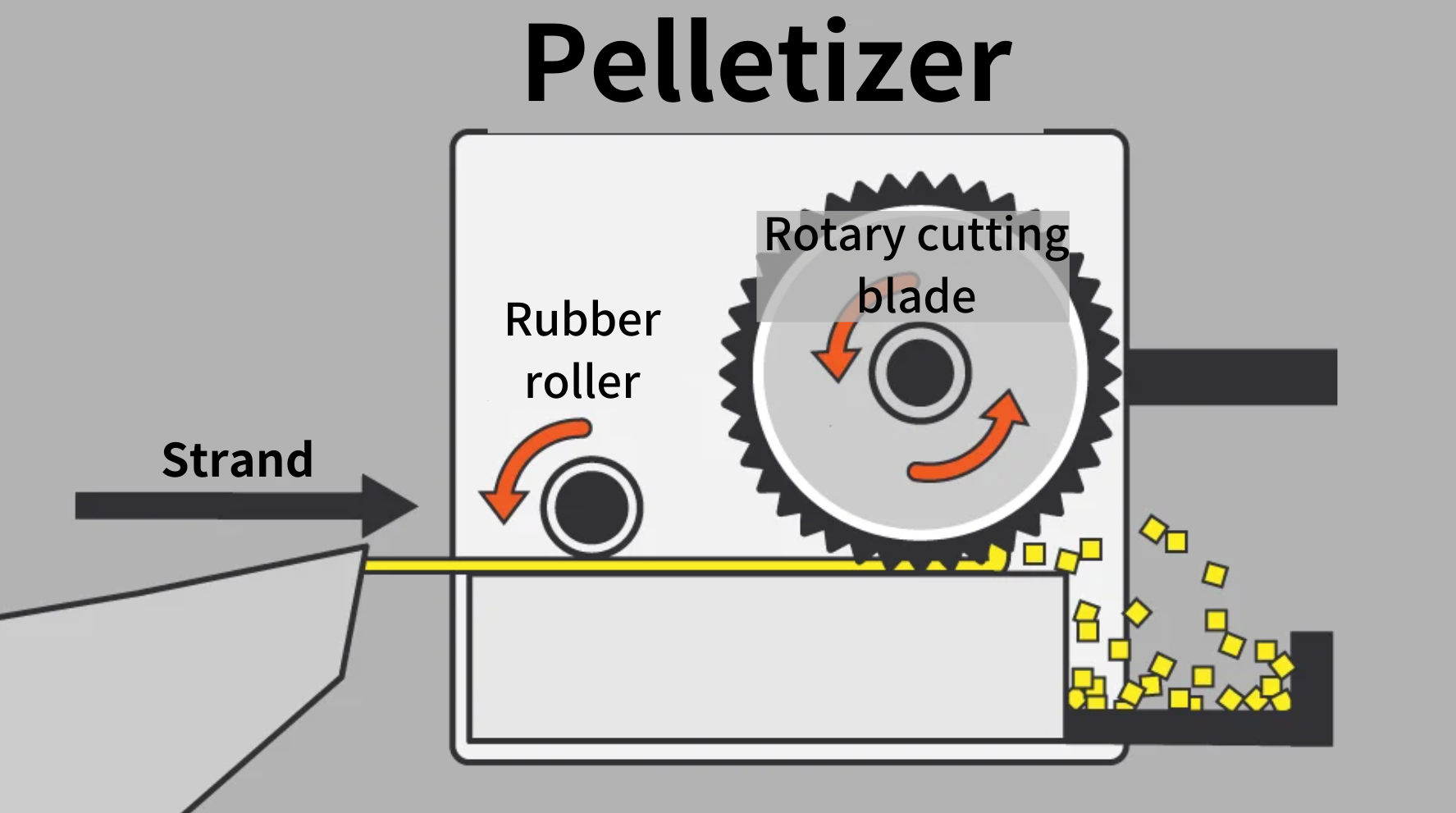
Strand pelletizer

Strand coming out of the die

Strand entering the pelletizer
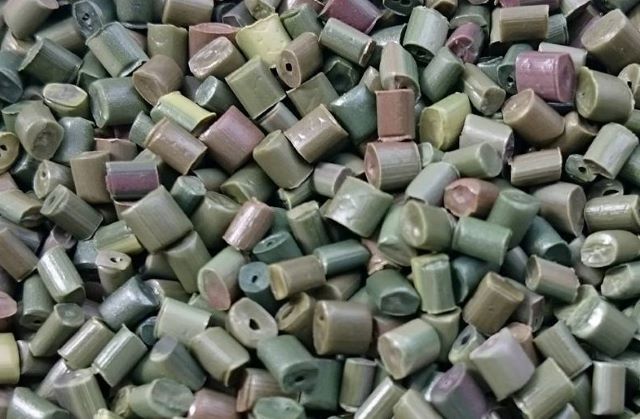

Cylinder-shaped pellets cut
Hot cut (watering cut)
A cutter rotating at high speed cuts the resin coming out of the die and discharges it with water for cooling. This is a pelletizing method that has increased in recent years.
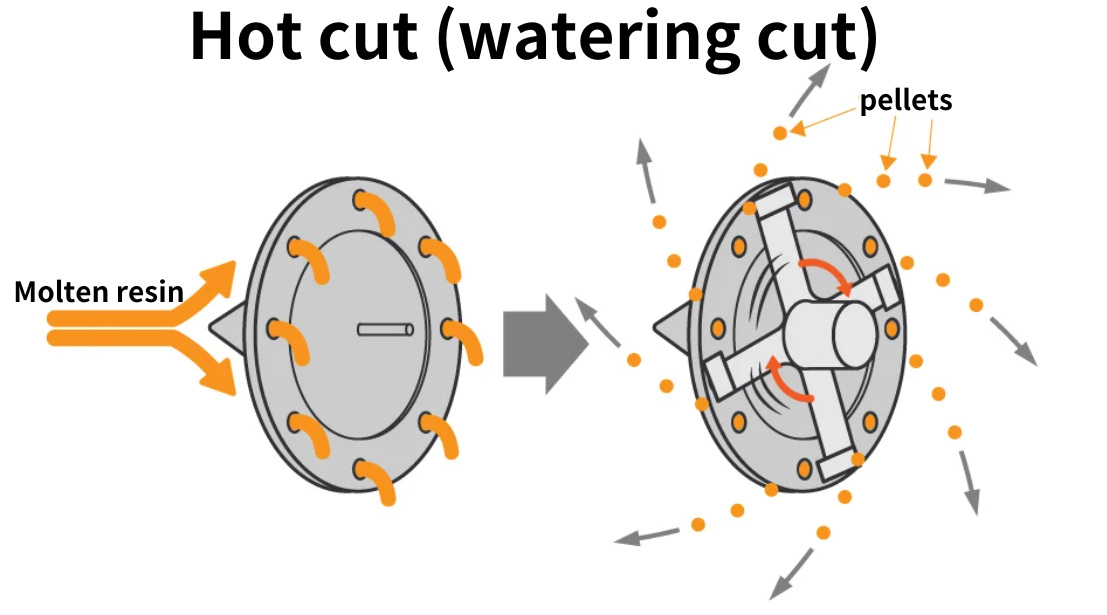

Hot cut method
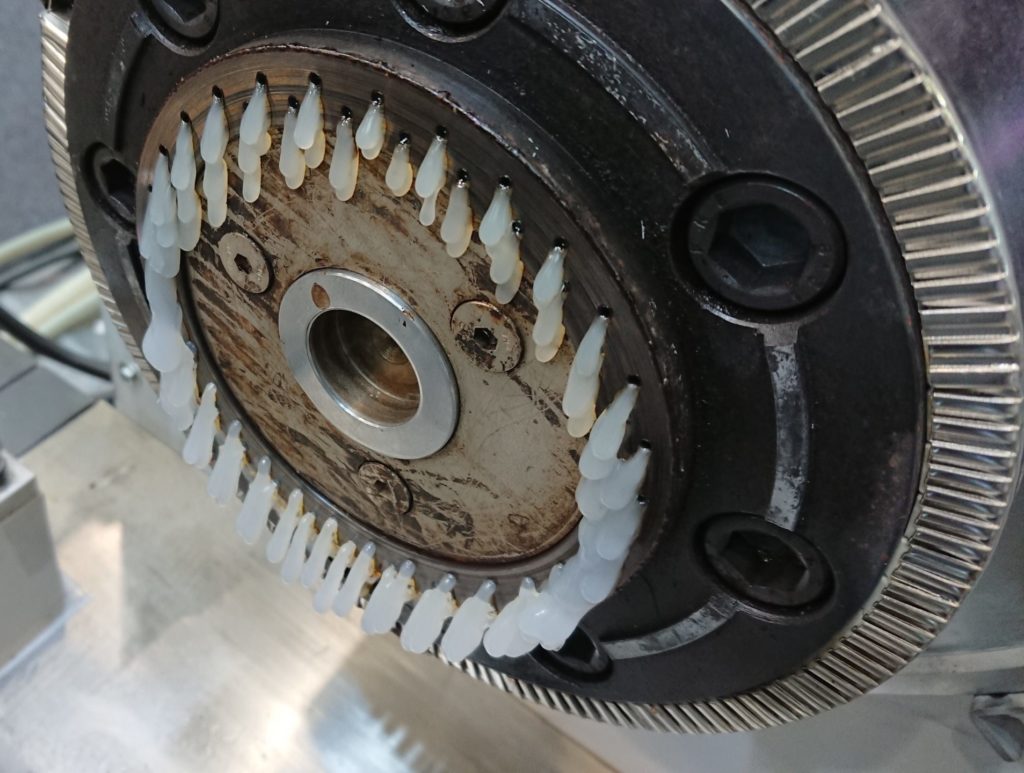
Resin that comes out of the hot-cutting die

Cut the resin with this cutter

Pellets cut into a round shape
Underwater cutting
Cut pellets directly from the die into water with a rotating cutter. This method is used for difficult resins and other materials. The equipment is more expensive than the above two methods.
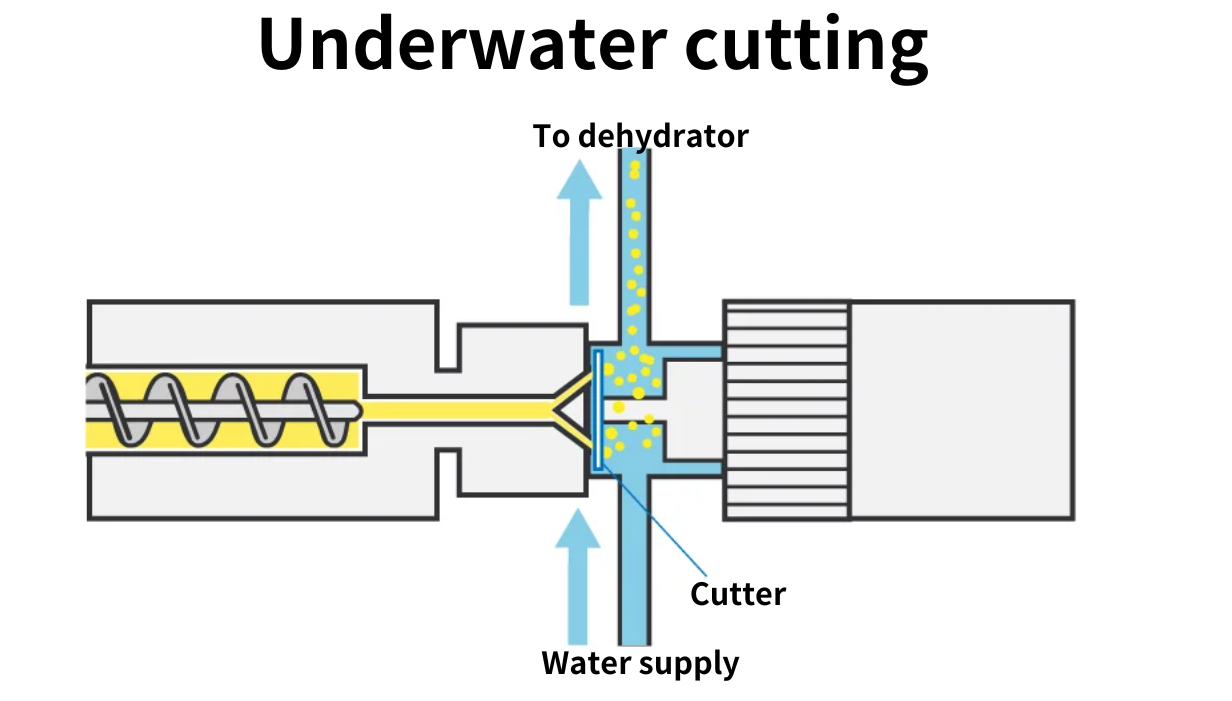
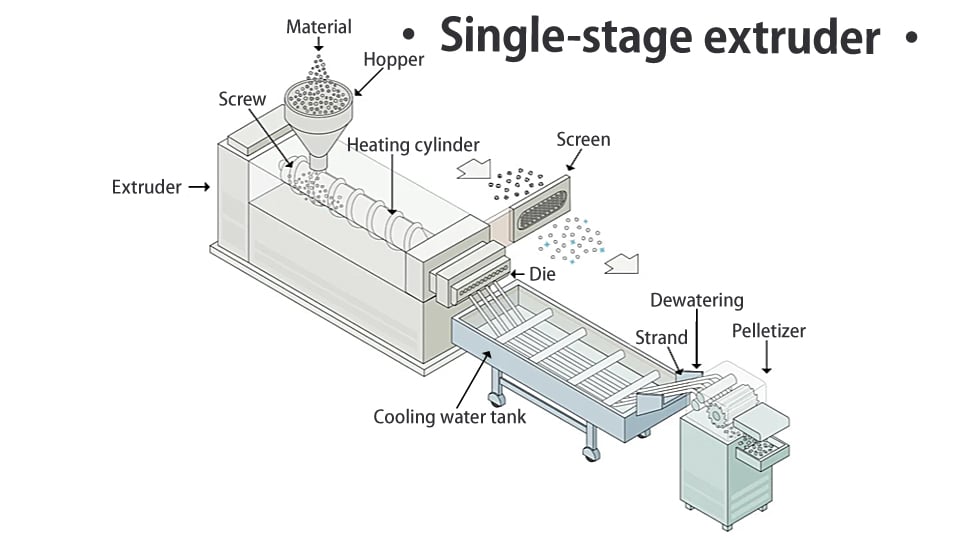
3) Classification by the number of extruders used in combination: single-stage and two-stage Single-stage extruder
Single-stage extruder
This is a line with only one set of extruder with screws and barrels. When processing various molded products, virgin raw materials, clean recycled materials, etc., it is almost always possible to process them without any problems using a single-stage extruder.
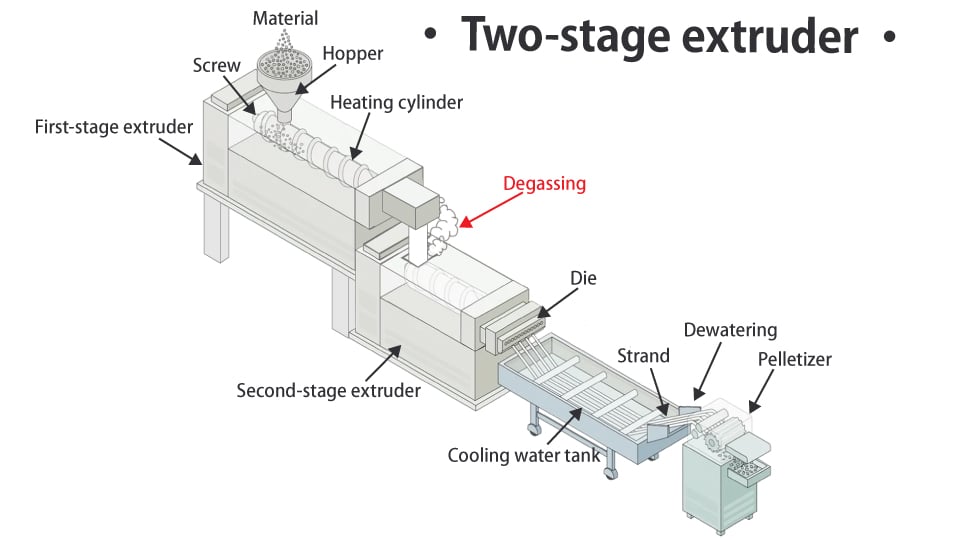
Two-stage extruder
Two extruders are connected to feed the resin from the first stage to the second stage after the resin is fully exposed to the air at the joint. It is mainly used in recycling sites. In recycling factories in China, a plastic recycling powerhouse, this two-stage extruder is used with a high probability.

Two-stage extruder
Two-stage extruder has the following advantages.
- Gas venting is excellent
Recyclable materials contain many causes of gas generation (moisture, ink, foreign matter). Then, materials that do not release enough gas will foam the pellets and become subject to claims. There are vents and vacuum pumps for gas venting, but they only have small holes in part of the cylinder. In the recycling site, there are many materials that cannot be vented enough with this alone. A two-stage extruder can release resin from the first stage into the air. Because it is fully open, it can release a large amount of gas. Naturally, the amount of gas that can be released is much larger in the latter case than in the former case where it is released from a small hole in the cylinder. It may be possible to solve even degassing that cannot be solved by vents or vacuum pumps.

The resin is fully opened when entering the second stage from the first stage, so the gas is released outstandingly
- It is possible to reduce surging.
The shape of the scrap varies greatly. Because there are differences in specific gravity, size, thickness, and the amount of ink (the source of gas), when melting scrap in a cylinder, the internal pressure often fluctuates. (Except for uniform scrap) If there are differences in the properties of the materials to be input, there will also be differences in the internal pressure of the cylinder. Then, the amount of resin coming out of the die at the tip of the cylinder also increases and decreases. (Surging occurs) With a single-stage extruder, pelletization is performed while this extrusion amount fluctuates, so the size of the pellets will be different. However, if there is another extruder (second stage) after the single-stage extruder, that second stage will average out the pressure, and resin will be extruded from the die of the second-stage extruder in a homogeneous and stable manner. This solves surging problems in recycled material granulation.
5. Extruder equipment
Feeder
The feeder of the extruder supplies raw materials to the screw of the extruder. To obtain a stable extrusion amount from the extruder, it is important to continuously supply a stable amount. If the amount suddenly increases or decreases, the amount coming out of the end of the extruder will also fluctuate. Fluctuations in extrusion amount are equivalent to fluctuations in quality and can become a major problem, so “stable feed” is a very important point. Common challenges include “bridging,” where materials become stuck like a bridge and do not fall, and unstable supply due to differences in material specific gravity.


Hopper
It plays a role in guiding and supplying resin materials to the screw by parts installed at the screw inlet of the extruder. Be careful not to cause clogging or bridging in this hopper.
For materials that are prone to bridging such as powder, methods such as aeration by air nozzles or destruction of bridges by giving impact with knockers are also considered as means to prevent bridges. It is also important to optimize the angle of the hopper according to the contents.
In general, the area directly below the hopper is where the material first enters, and heat is not applied to the screw or cylinder in this area. This is because if heated, the resin melts and solidifies, making it difficult for the material to bite. Instead of heating it up, there are cases where cooling water is circulated under the hopper for cooling purposes.
Volumetric feeder
This is a machine that automatically supplies materials to the hopper. A screw is attached to the bottom of the container, and this screw continuously discharges and supplies the material. The rotation speed of the screw can be controlled by an inverter, and this rotation speed adjusts the supply amount. If you do not check the rotation speed of the screw and the amount of pellets discharged, it will be difficult to supply accurately.
Also, when supplying materials blended with multiple raw materials in a tumbler or other device using a volumetric feeder, classification may occur in the container due to differences in specific gravity between multiple materials, resulting in materials that have been “mixed uniformly” in the tumbler not being uniformly mixed in equal proportions.
Gravimetric feeder
A gravimetric feeder is a system that supplies resin raw materials while measuring their weight. The blending ratio of the input raw materials is always constant in weight ratio, making it possible to manufacture products with stable quality.
Since there is no measurement by weight in volumetric feeders, it is not possible to manage how much of the input raw material is being supplied. By using a gravimetric feeder, it is possible to manage the raw materials from input to product. Even if the specific gravity of the material changes, it can stably supply materials with a constant weight ratio. However, it is expensive.
Cost reduction through quantitative feeder
Many factories still manually supply materials to feeders. By automating this process using “Quantitative feeder” it is possible to significantly reduce labor costs.
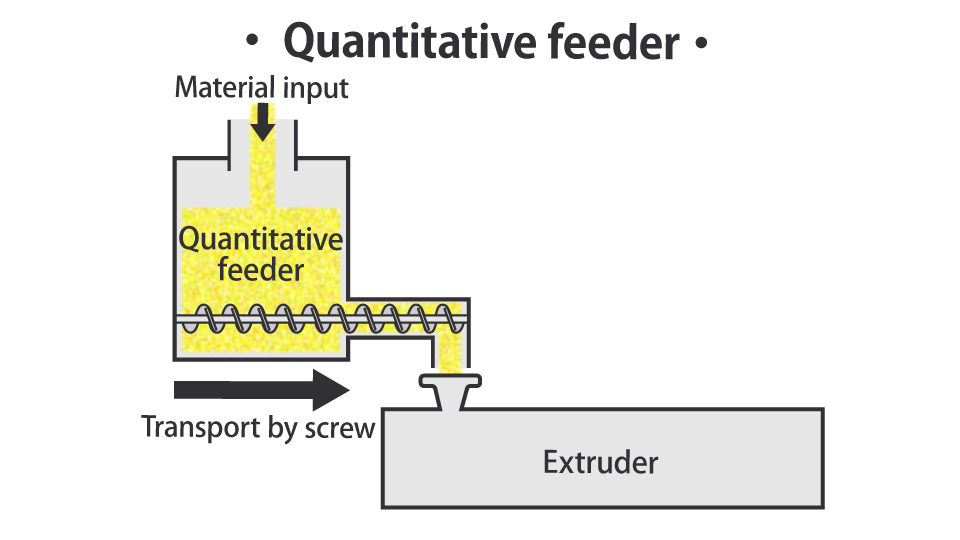
Side feeder
The side feeder method is a method of adding additives or masterbatches by screw from an inlet provided in the cylinder.
Normally, the raw materials are supplied to the hopper after being mixed in a tumbler or other device at a constant ratio. However, many operations are required to measure and add each material to the tumbler, tumble it, and then remove it before supplying it to the hopper. With the side feeder method, these blending steps can be eliminated, resulting in significant labor savings.


Liquid feeder
Used when injecting liquid additives.
Hopper dryer
Some resin materials undergo “hydrolysis” when they contain moisture. For resins that are easily hygroscopic, such as nylon, and resins that are easily hydrolyzed, such as PET, the hopper may be equipped with a dryer function.
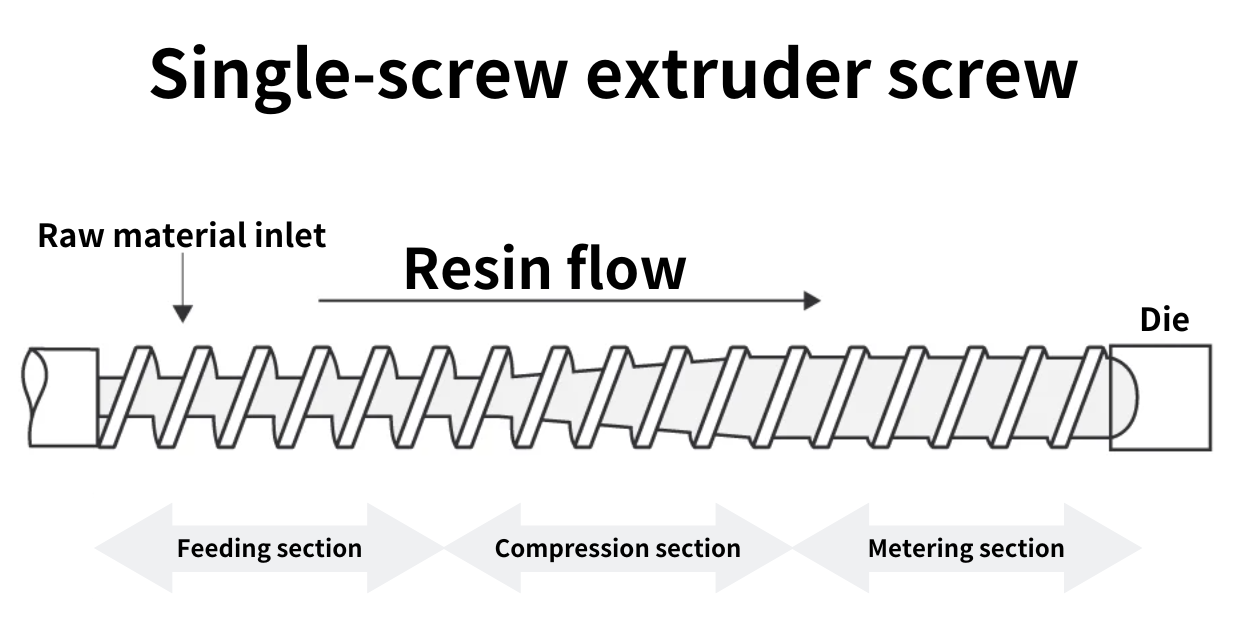
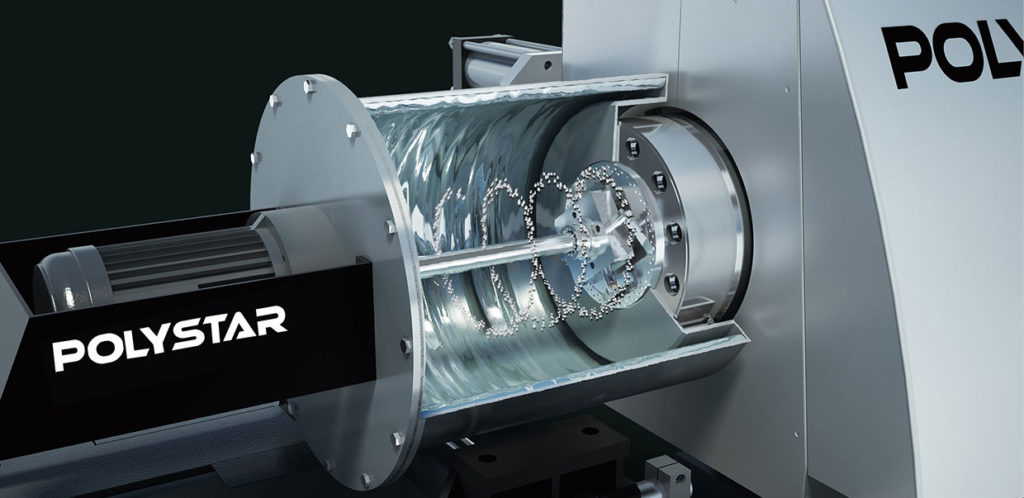
Screw of the extruder
The screw inside the cylinder melts the resin and carries it to the die at the end of the cylinder, where it is extruded by pressure. The structure and shape of the screw varies. The screw also causes a temperature rise due to shear of the resin. Its length is expressed in L/D (length-to-diameter ratio), and its material and material properties are selected appropriately for steel or heat treatment depending on the wear resistance of the material and the melting resin. There are one-axis screws that use a single screw and two-axis screws that use a pair of screws, which are used according to their purpose.
Reference article:A comprehensive explanation of the structure, length, thickness, design, and types of extruder screws used in plastic recycling.
Barrel (cylinder)
It is a cylindrical steel material that houses the screw that melts the resin of the extruder. The material is selected as a wear-resistant material or a corrosion-resistant material depending on the type of resin used and the type of filler added. The single-axis cylinder is cylindrical and made of one piece, while the two-axis cylinder is block-type, and these blocks are connected to form a cylinder.
Heating by extruder heater
Heaters are used to heat the cylinder of the extruder. There are different types depending on the purpose.
シリンダーに巻かれたヒーター
Band heater
A method of heating the surface widely by winding a heater that matches the cylindrical shape of the cylinder.
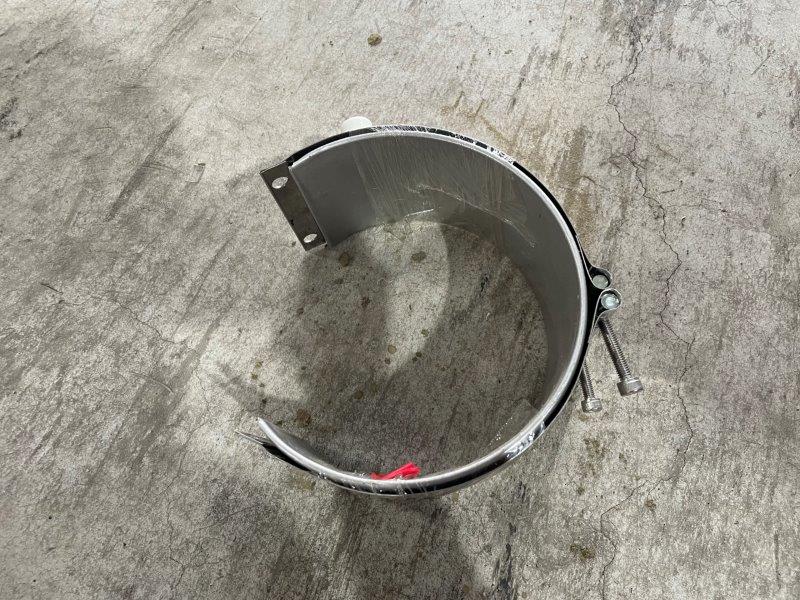

Ceramic band heater
It is effective to use a ceramic heater for resin raw materials that require higher temperature and higher watt density. It is used for resins with high melting temperatures or resins that contain moisture in recycling sites that need to be melted quickly. It lasts longer than band heaters despite being at high processing temperatures.
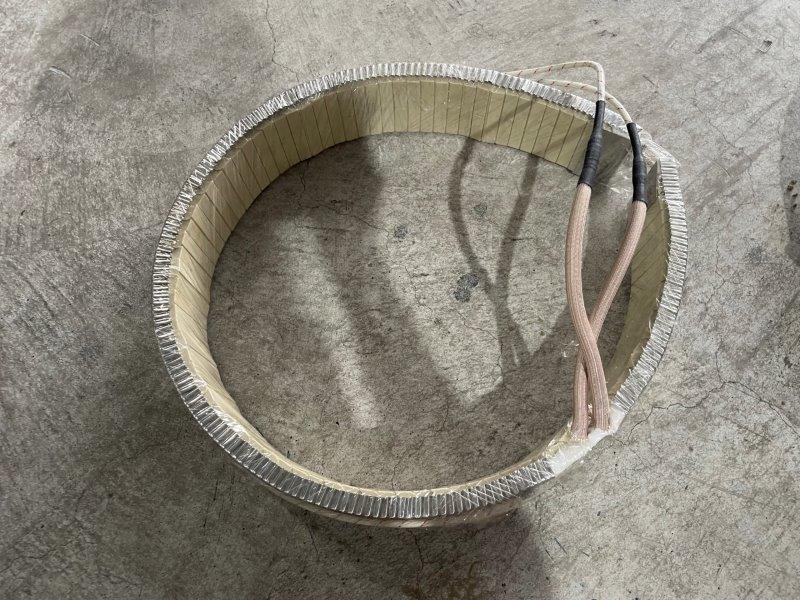

Cast-in heater
This is a heater that uses a cast aluminum mold to cast the heater. The cost is considerably higher than that of band heaters, but it provides stable performance when temperature management or uniform heating is required, such as for heating high-precision engineering plastics. It is also resistant to vibration and shock and can be explosion-proof. The aluminum and heater are in close contact, so it has good thermal conductivity and good heat distribution, making it long-lasting.
Vent
It is a vent hole that is open in the cylinder of the extruder commonly used in recycling and is a vacuum port. By removing steam and generated gas from the vent, product quality can be improved. Conversely, if gas generated cannot escape and remains in the pellets, the pellets will contain bubbles and cause a phenomenon called “foaming”.

Pellets that are not foamed
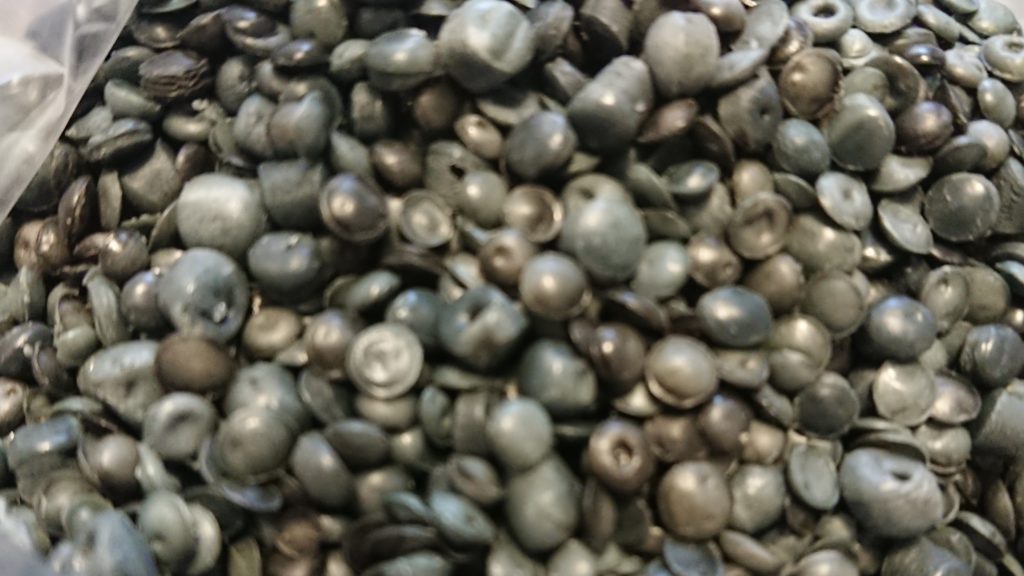

Pellets that are severely foamed
This foaming becomes a cause of various product defects when used by users of pellets, so “foamed” pellets are subject to claims. The vent is an opening provided to suppress such foaming and supply high-quality products.
Vacuum pump
Connect a vacuum pump to the vent to forcibly remove gas. It is more effective than just a vent and helps improve the quality of pellets and products produced. In addition, when processing resins that generate odors such as ABS, it reduces the odor that fills the work site and improves the work environment.
Multiple vents
There are cases where multiple vent openings are provided when a single vent cannot remove all the gas.
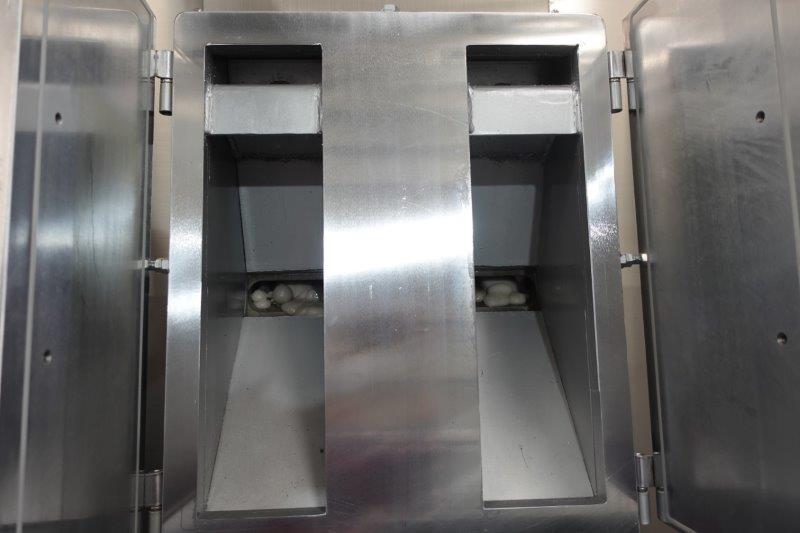


Screen changer
The screen is a metal mesh that is set at the tip of the cylinder and removes foreign matter and other resins mixed in with the melted resin. Usually, it ranges from about 20 mesh for the coarsest mesh to 200 mesh, and sometimes 500 mesh. In the recycling field, materials with a lot of foreign matter such as market-collected products often use about 20-40 mesh. In addition, when removing foreign matter carefully for film use, etc., it is often removed with 100-150 mesh. The screen changer is a device for replacing this screen (mesh). There are four types of screen changers, which are used depending on the amount of foreign matter.
Breaker plate
The breaker plate is a steel plate with many holes at the tip of the cylinder. It has two roles:
- Set the mesh (screen)
- Increase the back pressure flow in the cylinder and cause shearing, which improves the kneading of the resin.
By setting a mesh on the breaker plate, it is possible to remove foreign matter contained in the resin. In addition, by setting a mesh on the breaker plate, the back pressure is further increased, and a more well-kneaded resin is stably extruded from the die.
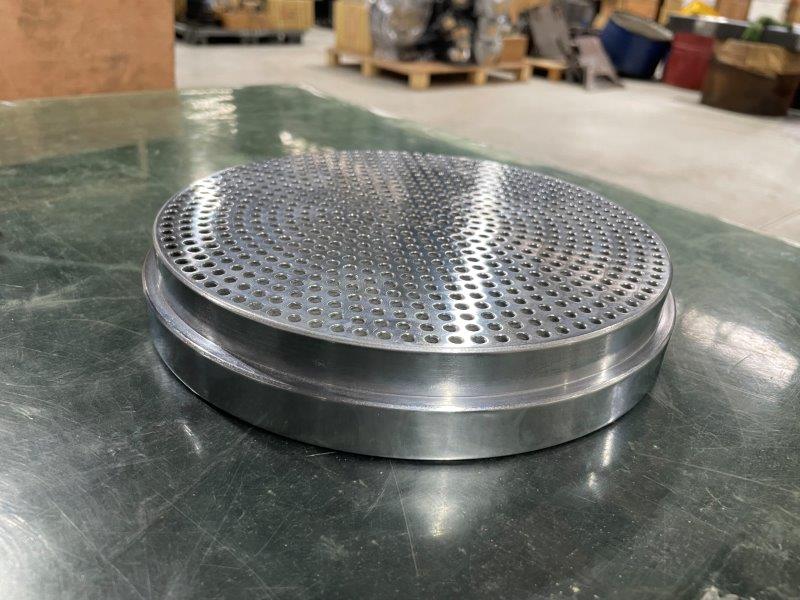


Die
The part at the tip of the cylinder in the extruder where the resin conveyed while being kneaded by the screw finally comes out. Depending on the shape of the mold (die) at this outlet, various types of products such as films, plates, injection-molded products, and pellets are formed.

Resin from hot-cut die
Dies are generally made streamlined to avoid stagnation at that part and prevent generation of scorching and other problems, and to make the flow, pressure, resin temperature, etc. uniform. The temperature of the die is also one of the factors that determine the molding of the product, so it is important to be able to finely control the temperature.
Strand
The illustration at the top of the page shows a cutting system using the strand method. The method of immediately putting the melted resin that comes out of the die hole into water in a tank and stretching it like long pasta and cooling it in the tank is called the strand method.
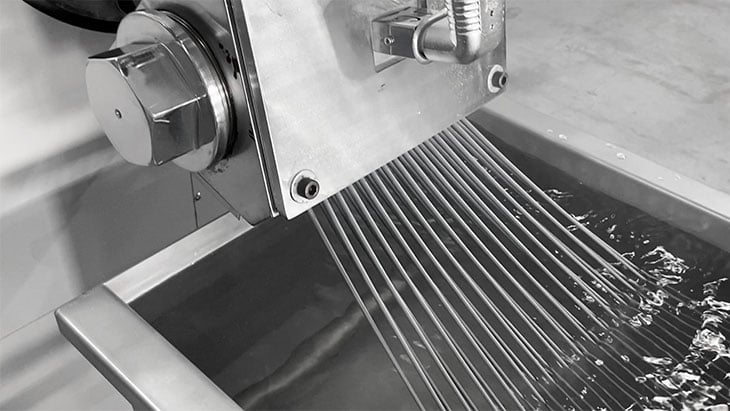

Strand pelletizer
Pelletizer
The structure of the pelletizer differs depending on whether it uses the hot cut method or the strand method.
Hot cut pelletizer
In the hot cut method, the rotating blade cuts the plastic on the surface of the die at high speed.
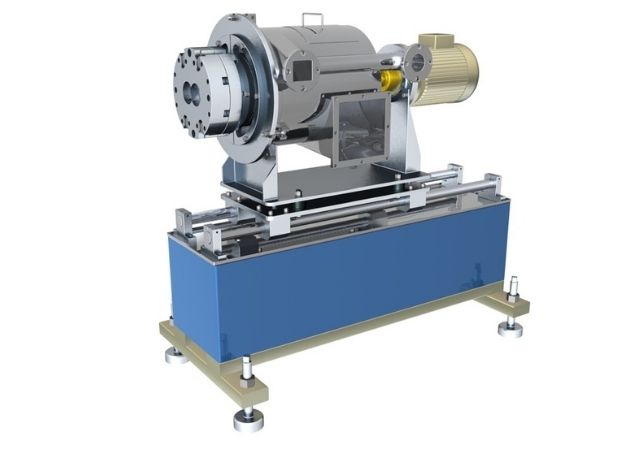
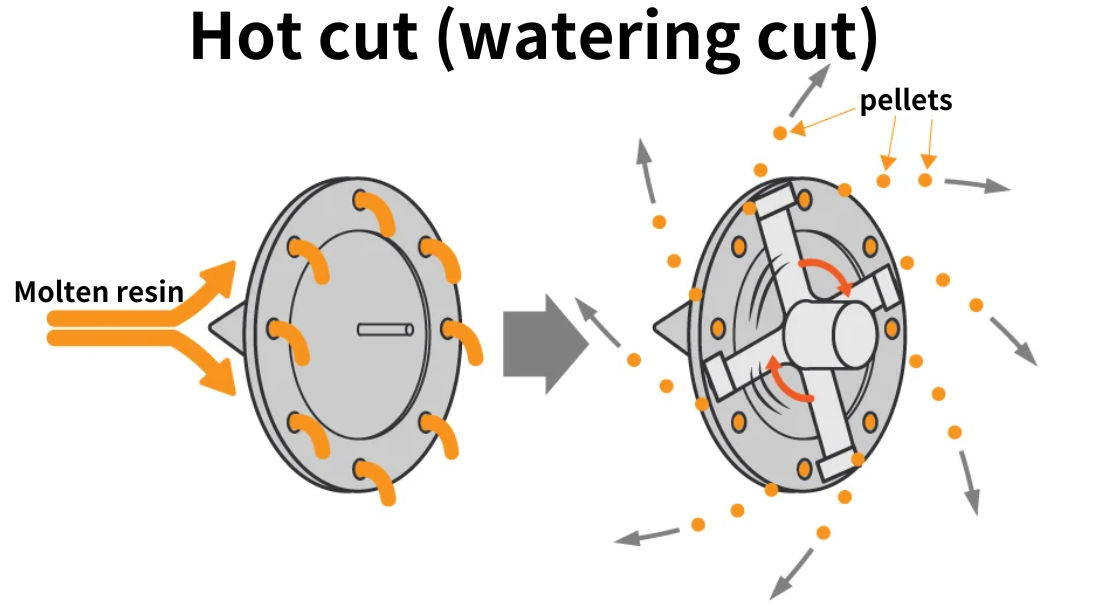

Hot cut pelletizer
Strand pelletizer
In the strand method, the cooled pasta-like resin is cut with a rotating blade.


Strand pelletizer
6. Streamlining and automation of extruder operation
The automation of extruders is essential for achieving stable extrusion with fewer people, which is closely related to profit margins. In the past, weighing and feeding work for extruders, screen replacement, and pellet packaging (packaging) work were done by hand, but recently automated equipment has become available.
Continuous Feeding System
Here is a method for continuously and automatically supplying materials without human intervention.
-
- Quantitative feeder: A tank that automatically and unmannedly supplies pre-processed crushed products to the extruder.
- Volumetric feeder: A feeding method that controls the supply by the rotation speed of the screw.
- Weight feeder: A method of feeding while measuring the weight.
- Side feeder: A continuous unmanned supply of material from the side of the cylinder by a screw.
- Ribbon blender: A tank that blends while supplying from the bottom screw.
- Cutter compactor: A method of continuously supplying materials to an extruder while crushing them with a rotating blade.
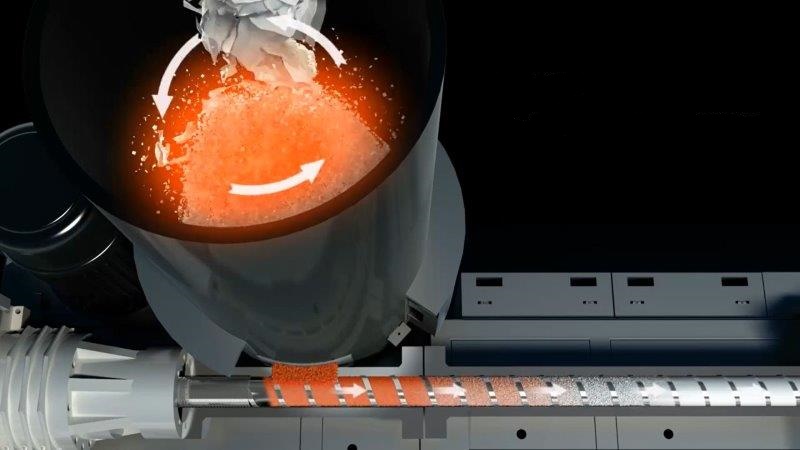

Cutter compactor
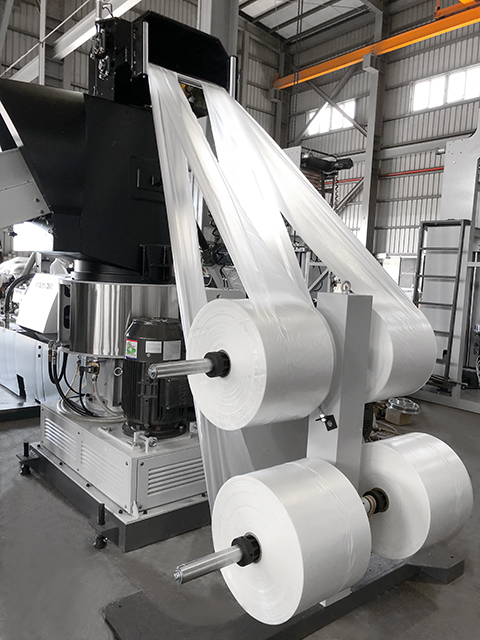
- Nip roller: A device that continuously takes up and supplies film rolls with rollers.

- Integrated extruder with crusher: A method of directly supplying scrap from a crusher integrated with an extruder to the screw of the extruder.
- Cutter compactor type: A method that allows film scraps to be directly fed into the extruder.
- Built-in crusher type: A method that allows molded products or dumplings to be pelletized as they are by simply putting them in a crusher.
Pelletizing automation
The following are the methods of pelletizing that do not require manual labor such as strand pelletizing.
- Hot cut method: A method in which a rotating blade cuts the resin the moment it comes out of the die.
- Underwater cutting method: A method in which the cutting by the rotating blade mentioned above is performed underwater.
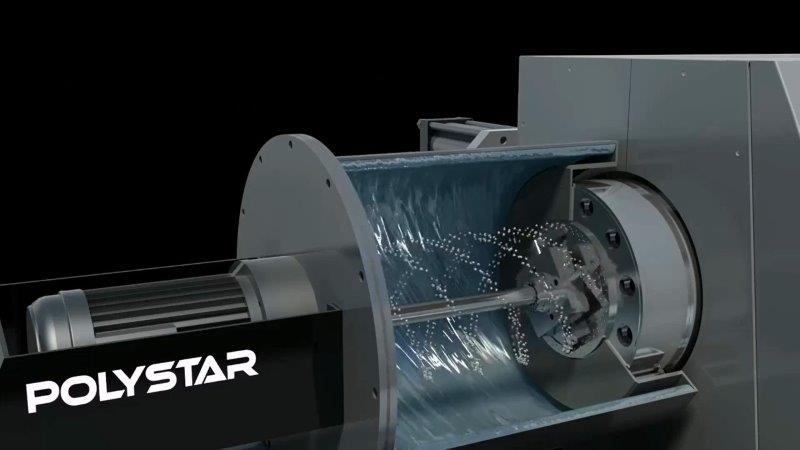
Underwater cutting method
Automated screen filter replacement
“Automated screen filter replacement” is a method of automating and streamlining the screen filter replacement process that usually requires manual labor.
- With the dual piston system:It is possible to continue operation without stopping even while replacing one of the screens (screen replacement is done manually).
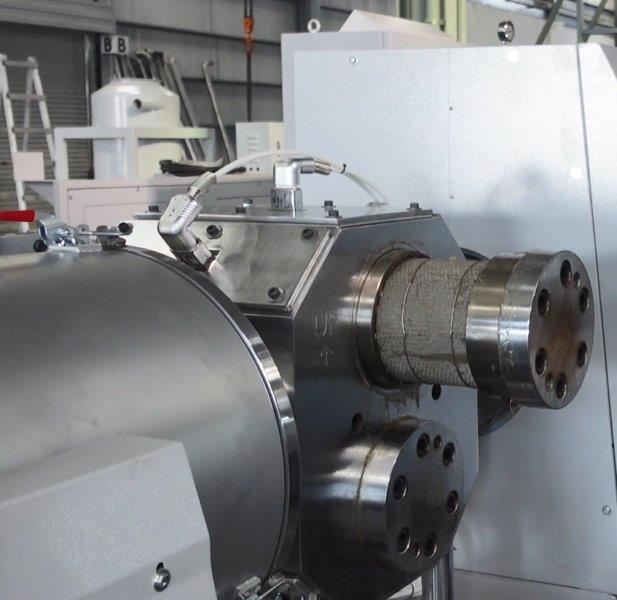

Here is a video of the screen replacement process.
- Laser filter:The laser filter uses a blade that rotates over the filter to automatically and continuously remove foreign matter.

Packaging
- Automatic measuring and filling system: Automatically measures and fills from the pellet silo tank.
7. Extruder and pellets
Changing the color or material of pellets
In the recycling process, there is little need for a severe material change. Especially for general-purpose resins such as PE, PP, PS, and ABS, the next resin is usually flowed without changing the material. After a while, the resin is considered to have “changed”.
However, when it comes to materials such as transparent or film materials and engineering plastics, more attention is required. In processing for high-precision products made of virgin raw materials, cleaning agents (purge materials) are used, screws are removed and cleaned, or baked at high temperatures to remove them. In some cases, chemicals are used to clean them.
Pellets and foreign matter
In the recycling process, various foreign matter and different resins are mixed.
It is not that you should not put foreign matter in the resin. Fillers such as charcoal powder or talc (stone powder), and wood powder are intentionally blended with the resin to manufacture raw materials. However, there are few things that have a good effect on things that come in as unintentional garbage. They are removed by a screen filter, but if there are too many of them, it takes time to replace them and labor costs increase.
- Paper: Causes carbonization or clogs the screen and causes complaints about the smell of burnt paper.
- Metal: Causes serious damage to extruder screws, cylinders, cutters, etc.
- Sand: Causes wear on screws and cylinders or clogs mesh.
- Soil: Same as above
- Organic matter: Causes mesh clogging or odor generation or carbonization.
- Different resins: Changes the physical properties of the resin. Resins that melt at high temperatures cause mesh clogging.
Pellets and Foam
Foam is a term used to describe the state of pellets that have some gas mixed in and contain bubbles.Foamed pellets are lighter than normal pellets and pellets with intense foaming are easily crushed when bitten.
If the user tries to manufacture their products using pellets with bubbles, gas will enter the product and defects will be found in the appearance of the product. Recyclers always check whether pellets are foamed or not because if they ship foamed pellets, they will receive many complaints.
Causes of foaming:
- Moisture in scrap: Moisture vaporizes in the cylinder. Resins with high water absorption contain moisture even if they do not appear wet (PA).
- Foreign matter: Foreign matter is overheated and gas is generated.
- Different resins: When melted to match the higher melting point, the resin with the lower melting point is gasified.
- Gas due to carbonization: Foreign matter clogged in the filter carbonizes and generates gas due to surface temperature rise.
- PVC: If PVC is mixed in, it will gasify when it exceeds 100℃. To reduce foaming, specifications such as vents, vacuum pumps, and two-stage extruders are adopted in extruders.
Burning of Pellets
Some people say that extrusion processing is a battle against burning. The resin is heated and melted in the cylinder, but burning may occur depending on the temperature and flow.
The causes of burning are said to be various, depending on overheating or resin retention. If there is residual material after processing, it often carbonizes inside. If carbon deposits adhere to the screw over a long period of time, the discharge volume may decrease.
Gelation
If the resin is retained for some reason, it becomes a cause of gelation or burning due to thermal decomposition. Retention is thought to be related to the shape of the flow path, such as screw design and die design. By making the flow path as streamlined as possible and making it simple in shape, retention can be prevented and gelation and burning can be prevented.
8.Trouble with extruder
Surging
It is a phenomenon in which the shape of strands or pellets changes due to the resin coming out of the die too much or too little. Surging occurs when the pressure inside the cylinder does not become constant due to differences in specific gravity, ink, size, etc. of the material. If surging occurs even though there is no problem with the material, it may be caused by wear of the screw.
It is also possible to suppress surging to some extent by making the extruder specification two-stage.
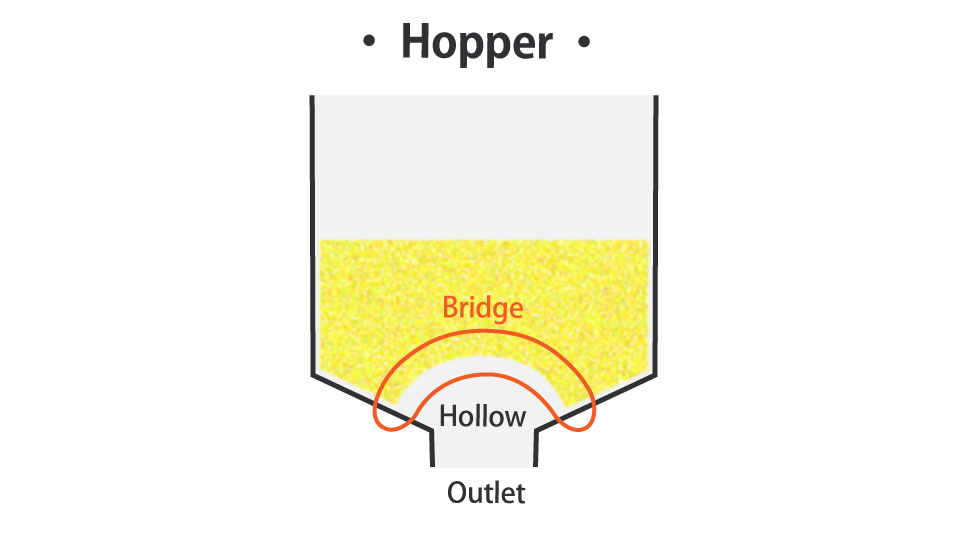
Bridge and rat hole.
It is a phenomenon in which only a part of the crushed product of film or sheet, powder-like material supplied from the hopper falls near the discharge port, and the upper part forms a “bridge” and does not fall (not supplied). If bridges occur frequently, it will affect productivity because it will cause problems with continuous production and require personnel to recover it every time.
There are feeders for powders that are less likely to cause bridging and side feeders for film crushed products.
Vent up
It is a phenomenon in which resin comes out of the hole for vacuuming in the cylinder. The direct cause is that the resin does not flow from the tip to the front due to clogging of the die, clogging of the screen mesh, water vapor due to moisture, etc., and the resin is released from the hole where it is released due to an increase in back pressure. It comes out. It is possible to suppress it by replacing the screen early while checking with a pressure gauge so that the screen does not clog. Recently, screens that automatically discharge foreign matter have also been released.
Even if it is called an extruder in one word, the materials to be processed and the shape and condition of scrap are all different. To produce efficiently and without trouble, it is important to select an extruder with a structure that suits each one.
8. Q&A about extruders.
Is a heater used to melt the resin?
In fact, the heater is not used much during operation. The shear heat is generated from the resin by rotating the screw with a motor, so it uses that heat during operation. For resins where strong shear occurs, the temperature can rise too much due to shear heat.
How do you use the single-screw and twin-screw of the extruder?
In plastic recycling, single-screw extruders are used almost exclusively. The purpose is to granulate plastic scrap. Twin-screw extruders are often used for compounding, which involves mixing colorants or additives, modifying resins, and blending various resins. In short, if you want to “knead well,” choose a twin-screw extruder. If you want to “make pellets anyway,” choose a single-screw extruder.
When do you use a two-stage extruder?
A two-stage extruder is rarely used when processing virgin materials. The two-stage extruder is used in recycling. In particular, it is often chosen when there are many foreign substances, when there is moisture, or when there is a lot of printing ink in the scrap. By using a two-stage extruder, even poor-quality materials can be produced stably.
Which is better, hot cut or strand?
Both have their advantages and disadvantages. In short, if the material is of good quality and stable, strand is fine. For labor-saving or processing materials with foreign substances mixed in, hot cut is chosen. Hot cut can pelletize even if there are some foreign substances mixed in, so some users of recycled pellets dislike hot cut and prefer strand.
9. List of extruder manufacturers
High price range
- Japan Steel Works, Ltd. (Japan,https://www.jsw.co.jp/en/)
- Shibaura Machine Co., Ltd. (Japan,https://www.shibaura-machine.co.jp/en/)
- CTE Co., Ltd. (Japan,http://www.cte-japan.net/en/)
- Technovel Corporation (Japan,https://www.technovel.co.jp/en/)
- Ikegai Corporation (Japan,http://www.ikegai.co.jp/en/)
- Coperion GmbH (Germany, https://www.coperion.com/en)
- Leistritz AG (Germany, https://www.leistritz.com/en/start)
- Milacron Inc. (Germany, https://www.milacron.com/)
Medium price range
- SINO-ALLOY MACHINERY INC.(Taiwan, https://www.sinoalloy.com/en/home-2/)
- Zenix Industrial Co., Ltd.(Taiwan, https://www.zenix.com.tw/)
- POLYSTAR MACHINERY INC (Taiwan,https://www.polystarco.com/en/about_C03.html)
- Freesia Macross Corporation (Japan, http://www.freesiamacross-extruder.com/en/)
Low price range
- NANJING COWIN EXTRUSION MACHINERY CO.,LTD.
(China, https://www.cowinextrusion.com/) - STEER Engineering Pvt Ltd(India, https://www.steerworld.com/)

Comment